Written by Helen Lewis

Nurses are the backbone of the American healthcare system.
As a nurse, it can be meaningful to know that you serve an essential role in the functioning of any hospital or medical practice. At the same time, the high stress, intensity, and emotional nature of nursing work can take a significant toll on nurses, one that is often under-discussed.
When nurses are well-rested, mentally healthy, and feel supported, they are able to provide the attentive, compassionate care that patients need. This not only helps with better patient outcomes but also enhances the overall experience for patients experiencing their own feelings of vulnerability in a healthcare setting.
The following article begins by underlining the direct connection between the mental wellness and job performance of nurses. Then, it touches on various avenues for mental health support for nurses, providing extensive information about available resources that support burnout prevention and stress management. This article also touches on cost-effective and even free mental health resources available to nurses, such as apps and crisis hotlines.
Nurse Wellbeing: A Cornerstone of Effective Care
When nurses are in a positive state of wellbeing, they have the physical stamina, mental clarity, and emotional resilience needed to handle the many demands of their job.
Nursing is both an incredibly rewarding and a highly challenging profession, requiring long hours, intense focus, and emotional intelligence.
When nurses are burned out, stressed, or overworked, it can significantly affect the quality of care they provide.
Fatigue can lead to mistakes in administering medication, slower response times, and difficulty in making critical decisions—all of which can jeopardize patient safety. When nurses are over-stressed or emotionally drained, it can be harder for them to connect with patients on a human level, potentially leading to a less compassionate and supportive environment. This is especially important because patients often look to nurses not just for medical care, but also for comfort and reassurance during difficult times.
By contrast, happy, healthy nurses are more likely to stay in their jobs longer, reducing turnover and maintaining continuity of care. They’re also better equipped to collaborate effectively with other healthcare professionals, which is essential for delivering cohesive and comprehensive care.
Mental Health Challenges in Nursing
The intense pressures of the job—long hours, emotional labor, and the responsibility of caring for critically ill patients—can take a serious toll on nurses’ mental wellbeing, including burnout, anxiety, depression, and even PTSD.
Studies have shown that nurses are at a higher risk for mental health issues compared to the general population, with some reports indicating that nurses are twice as likely to experience depression and are at a higher risk for suicide.
When nurses are struggling mentally, it can lead to increased medical errors, decreased job satisfaction, and higher turnover rates, which add further strain to the healthcare system.
The COVID-19 Pandemic and Extreme Stress for Nurses Across America
The COVID-19 pandemic placed unprecedented demands on nurses, requiring them to work long hours in high-risk environments with a constant influx of critically ill patients.
At first, many nurses were working without adequate personal protective equipment (PPE), which heightened their fears of contracting the virus and spreading it to their families. This, combined with the emotional burden of seeing so many patients suffer and die, led to severe burnout, anxiety, and even symptoms of PTSD among nurses. The pressure to make quick, life-or-death decisions in a chaotic environment further exacerbated their stress levels.
The mental health impact of this extreme stress was significant, highlighting the critical need for better mental health support and resources for nurses to help them cope with the long-lasting effects of the pandemic.
Psychological Support and Mental Health Assistance for Nurses in California: An Overview
This article intends to demonstrate to nurses who may be struggling with feelings of burnout, depression, or anxiety that they are not alone, and that there are many resources available to meet their needs.
For example, the California Board of Registered Nursing offers support groups aimed at helping nurses struggling with mental health or substance abuse issues, providing a crucial lifeline while enabling them to continue practicing safely. Additionally, the American Nurses Association of California has been actively involved in advocating for better mental health resources, focusing on reducing stigma and making support more accessible.
The Dr. Lorna Breen Health Care Provider Protection Act, signed into law in 2022, is another significant development in supporting the mental health of nurses in California and beyond. This federal law was created to address the mental health crisis among healthcare workers, including nurses, by funding programs that offer evidence-based mental health treatments and resilience training. While the act has already provided substantial resources, ongoing efforts are focused on expanding its reach to more healthcare facilities across California, ensuring that even more nurses can benefit from these critical services.
Moreover, California has been proactive in promoting mental health awareness through statewide campaigns like those run by the California Mental Health Services Authority (CalMHSA). These campaigns aim to reduce stigma, increase knowledge, and improve access to mental health services across diverse communities, including healthcare workers.
Free Resources for Nurses: Calling a Mental Health Hotline
Mental health support hotlines are a vital resource for nurses, offering immediate, confidential assistance when they need it most. One of the most widely recognized resources is the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline, which is available to the general public. By dialing 988, nurses can access immediate help if they are experiencing a crisis or feeling suicidal. The lifeline offers confidential support from trained counselors who can provide emotional support, crisis intervention, and referrals to additional mental health resources.
Mental Health Apps for Healthcare Professionals
In addition to crisis hotlines and free mental health programs for nurses, there are a number of apps available to smartphone users who may be interested in a modern, multimedia approach to mental health care. Examples of popular mental health apps include:
- Headspace: Offers guided meditation and mindfulness exercises to help reduce stress and improve mental wellbeing. The app is known for its user-friendly interface and variety of meditation programs tailored to different needs.
- Calm: Focuses on relaxation, sleep, and meditation. It includes breathing exercises, sleep stories, and calming music, which can be particularly useful for nurses dealing with anxiety or insomnia.
- Moodfit: A comprehensive mental health app that allows users to track their mood, set goals, and access cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) exercises. It also includes resources for stress management and emotional resilience.
- Sanvello: Provides on-demand help for stress, anxiety, and depression through guided journeys based on CBT. It includes mood tracking, guided meditation, and a community feature where users can share experiences and support one another.
- MyStrength: Offers personalized programs that address stress, anxiety, depression, and substance use. The app provides tools for tracking mental health progress, mindfulness exercises, and inspirational content.
- Talkspace: An online therapy platform that connects users with licensed therapists through text, voice, or video messaging. While there is a cost for therapy sessions, the app offers free resources such as mental health assessments and coping tools.
- Happify: Focuses on improving overall happiness through evidence-based games and activities designed to combat negative thoughts and stress in the aim of building emotional resilience.
- Mindshift CBT: Specifically designed to help users manage anxiety, Mindshift CBT offers CBT-based tools for tackling worry, panic, and other anxiety-related issues. It also includes relaxation exercises and thought journals.
These apps are readily available on both iOS and Android platforms. While some involve premium subscription content, many offer free versions or trials for those interested in lower-commitment or more cost-effective tiers.
Burnout Prevention for Nurses
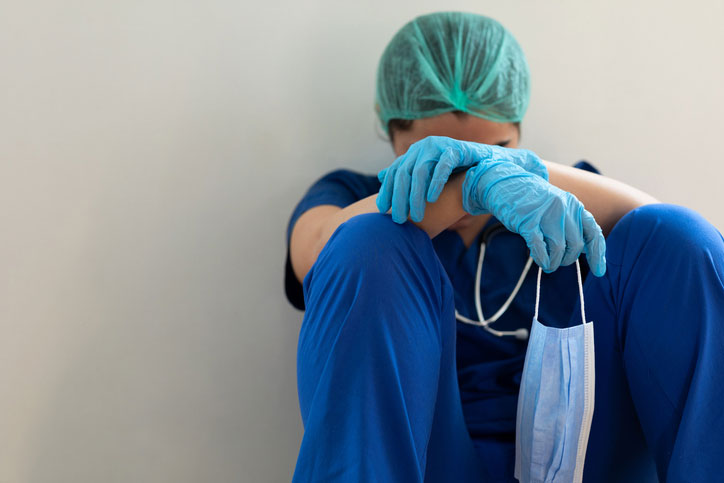
Burnout not only affects the well-being of nurses but also compromises patient care, as it can lead to increased errors and decreased empathy.
Burnout among nurses is a significant and growing concern, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. It manifests as physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged stress and overwork, often leading to feelings of helplessness, detachment, and a decline in job performance. Addressing burnout requires both individual strategies, like mindfulness and self-care, and organizational changes, such as reducing workloads and providing better mental health support.
One of the most effective ways to combat burnout is by addressing the underlying causes that contribute to it, such as heavy workloads, long hours, and the emotional toll of patient care. According to recent studies, providing nurses with a supportive work environment, where they feel valued and have a sense of control over their workload, can significantly reduce burnout. This can include implementing flexible scheduling, reducing unnecessary administrative tasks, and ensuring that nurses have access to mental health resources tailored to their needs.
Additionally, promoting a culture of self-care and resilience within healthcare settings is vital. Hospitals and healthcare organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of offering programs that focus on stress management, mindfulness, and peer support. For example, the CDC’s Impact Wellbeing initiative is a national campaign aimed at improving the mental health of healthcare workers by fostering healthier work environments. This includes creating structured, long-term plans to boost staff morale and integrating professional wellbeing into quality improvement processes. By combining individual support with systemic changes, these strategies help nurses manage stress more effectively and prevent the severe consequences of burnout.
Stress Management for Nurses
On an individual level, nurses can benefit from techniques like mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and physical activity, all of which help in reducing stress and promoting mental clarity. Regular exercise, even something as simple as a brisk walk, can significantly lower stress levels and improve mood. Mindfulness practices, which involve staying present and focused on the moment, have been shown to reduce anxiety and prevent burnout by helping nurses manage the emotional demands of their work more effectively.
However, stress management is also essential on the organizational level, a setup in which healthcare facilities work to create environments that reduce stress for workers. This includes providing access to mental health resources, such as counseling services or employee assistance programs, and encouraging a culture where taking breaks is seen as a necessary part of maintaining high-quality care rather than a luxury. By addressing these systemic issues, healthcare organizations can help create a work environment where nurses are better equipped to handle stress, ultimately leading to improved patient care and nurse satisfaction.
Nurse Counseling Services
In California, several counseling services are available to support nurses who are dealing with the mental and emotional challenges of their profession.
One valuable resource are the Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) offered by many healthcare organizations across California. These programs typically include free, confidential counseling sessions, either in person or over the phone, that are available to nurses as part of their employment benefits. EAPs provide support for a wide range of issues, including anxiety, depression, relationship problems, and work-related stress.
Crisis Support and Suicide Prevention for Nurses
In California, and across the country, nurses can access a variety of crisis support services designed to provide immediate help during particularly challenging times. One such service is the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline (988), which offers 24/7 support for anyone in crisis, including nurses. This hotline provides immediate, confidential assistance from trained counselors who can offer support and guide nurses through difficult moments. It’s an invaluable resource for those who might be experiencing overwhelming stress, anxiety, or thoughts of self-harm.
Additionally, many hospitals and healthcare organizations offer specific crisis support tailored to healthcare workers, including nurses. For example, some institutions have established crisis hotlines or peer support programs where nurses can speak with colleagues who understand the unique stressors of the job. These peer support programs often provide a more relatable form of help, as they connect nurses with other professionals who have firsthand experience in similar situations.
Concerned nurses and healthcare workers who prefer to text rather than speak over the phone can contact the Crisis Text Line, which allows nurses to reach out for help via text message. By texting “HELLO” to 741741, nurses can connect with a trained crisis counselor who can provide immediate support and guide them through their crisis. This service is available 24/7 across the U.S.
Finally, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) offers a free, confidential, 24/7 National Helpline (1-800-662-HELP) for nurses dealing with substance abuse or mental health crises, providing referrals to local treatment facilities, support groups, and community-based organizations.

Fostering Workplace Wellness in High-Stress Healthcare Environments
High-stress settings, such as hospitals and emergency departments, demand a lot from healthcare professionals, both physically and emotionally. To counteract the intense pressures of these environments, organizations must prioritize creating a supportive culture that promotes mental health and resilience. This includes implementing regular wellness programs, offering access to mental health resources like counseling services, and encouraging practices such as mindfulness and stress management techniques. These initiatives not only help reduce burnout but also enhance job satisfaction and retention, creating a more sustainable workforce.
Leadership also plays a critical role in fostering workplace wellness. Hospital administrators and department heads – which includes trained DNPs – must be proactive in recognizing the signs of stress and burnout among their staff and should work to create a culture where taking breaks, seeking help, and discussing mental health are normalized.
By providing flexible scheduling options, reducing unnecessary administrative burdens, and fostering open communication, leaders can help create an environment where healthcare workers feel supported and valued. This holistic approach to workplace wellness is crucial for maintaining the mental and physical health of healthcare professionals, ensuring they can continue to provide high-quality care to patients.
